LONG CASE
A 30-year-old male electrician by occupation from Nakrekal came to the hospital with chief complaints of weakness in the right upper limb and right lower limb since 15 months
Difficulty while speaking since 15 months
History of present illness:
Patient was a 30 year old electrician who used to climb up the cell towers for repair works
Born in the middle order with one elder brother & one younger brother
His daily routine include waking up at 7-8 am and going to work at 9am after having breakfast and returning home at 6-7 pm after a tiring work for 7-8 hrs
Married at the age of 25 yrs and has 2 children and used to live happily with his family & friends
But 15 months back his whole life was turned upside down when he developed sudden onset weakness in right upper limb & lower limb with mouth deviation to left side due to which he was not able to do his daily work of living & earning and he became dependant on family members
Patient was apparently asymptomatic 15 months back and then he developed weakness in the right upper limb and right lower limb which was sudden in onset and associated with on and off difficulty in speech.
Weakness was predominantly on the right arm than the right leg.
History of difficulty in speaking since 15 months - patient describes it as not able to tell what he wants to tell but able to write it down (word-finding pauses)
History of difficulty in buttoning the shirt, mixing the food, and writing present
History of slippage of footwear present
No difficulty in squatting and getting up from the squatting position, climbing stairs up and down
There was no diurnal variation of weakness
No difficulty in lifting the head off the pillow
No difficulty in rolling over the bed, getting up from the bed
No difficulty in breathing
No history of pain or muscle cramps or fasciculations and any involuntary movements
Able
to feel clothes, feeling hot and cold water while bathing
No history of tingling, numbness, pricking-like sensation, band like sensation or sensation of walking on cotton wool
No history of neck pain, or back pain
No history of unsteadiness on closing his eyes and is able to walk in the dark
No history of loss of consciousness or alteration in sensorium or any bowel bladder involvement.
No history of Delusions/ Hallucinations/emotional disturbances
No history of alteration of smell, blurring of vision, diplopia, difficulty in chewing, hearing difficulties or dysphagia.
No history of giddiness, syncope, sweating, or palpitations
No history of bowel or bladder incontinence
No history of fever, headache, vomiting, or neck stiffness.
No history of calf pain, trauma, fall from height, or any drug intake.
Past history:
No history of similar complaints in the past.
No comorbid illness like Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, coronary artery disease, thyroid disease, HIV, Tuberculosis, malignancy, or surgeries.
Personal history:
Married And non-vegetarian with normal sleep and appetite.
No alcohol and smoking habits.
Regular bowel & bladder habits
Family history:
Nonconsanguinous marriage, With no similar complaints in the family.
No significant past treatment history.
Summary:
Onset: Acute
Progression: rapidly progressive
Neurological: Right hemiparesis with UMN-type facial Nerve involvement
Anatomical: cortex > subcortical
Etiology: secondary to vascular > inflammatory.
General examination:
Patient conscious, coherent, and oriented to time place person
Moderately built and nourished
No pallor, icterus, clubbing, koilonychia, lymphedema, and pedal edema.
Temperature: Afebrile
PR: 78 bpm, regular, normal in volume and character with no radio radial delay or radio femoral delay.
BP: 130/80 mm hg in the right and left arms.
RR: 16 CPM
Systemic examination:
Central nervous system:
Higher mental functions:
Level of Conscious Normal (GCS: 15/15)
Oriented to time place and person.
Speech and language :
spontaneous speech present
Comprehension present
Fluency absent
Repetition absent
Reading and writing present
Cranial Nerve Examination:
1st Cranial Nerve (Olfactory):
Sense of smell present
2nd Cranial Nerve (Optic):
Visual acuity, Field of vision, and color vision are present. Fundus is normal.
3rd,4th, and 6th cranial Nerves (Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducens):
Extraocular movement And pupil size normal
Direct and indirect light reflexes present and accommodation reflex present
No ptosis and nystagmus
5th cranial Nerve (Trigeminal):
Sensations over the face present
Corneal conjunctival reflex present
7th Cranial Nerve (Facial):
Motor: Nasolabial fold absent on the right side
Orbicularis occuli and frontalis muscle normal
Tongue Sensations Normal
Corneal and conjunctival reflexes present
8th Cranial Nerve (Vestibulo-Cochlear):
Rinnes test and Weber test- No hearing loss.
9th and 10th cranial Nerve (Glossopharyngeal and Vagus):
Uvula and Palatal arch movements are normal and the gag reflex is present.
11th cranial Nerve (Spinal accessory):
Sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle normal
12th Cranial Nerve (Hypoglossal):
Tongue protrusion in the midline.
Gait: Hemiplegic circumduction gait
Motor System:
Bulk:
Inspection: Right thigh appears to be atrophied
Measurements:
Upper limb:
Right side 27.5 cms @ 10 cms above the olecranon & 24 cms @ 10 cms below the olecranon
Left side 29.5 cms @ 10 cms above the olecranon & 26 cms @ 10 cms below the olecranon
Lower limb:
Right side 46 cms @ 18 cms above the superior border of patella & 33 cms @ 10 cms below the tibial tuberosity
Left side 50 cms @ 18 cms above the superior border of patella & 33 cms @ 10 cms below the tibial tuberosity
Right. Left
Tone:
Upper limb. Normal Normal
Lower limb. Normal Normal
Power:
Upper limb:
Proximal muscles 4/5 5/5
Deltoid
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Biceps
Triceps
Brachioradialis
Pectoralis and latismus
Dorsi muscle
Rhomboidus
Distal muscles. 0/5 5/5
ECR
ECU
Extensor digitorum
FCR
FCU
Lower limb:
Proximal muscles 4/5 5/5
Iliopsoas
Adductor femoris
Gluteus maximus
Gluteus medius and
minimus
Hamstrings
Quadriceps femoris
Distal muscles. 0/5 5/5
Tibialis anterior
Tibialis posterior
EDL
FDL
EHL
EDB
Reflexes: Right Left
Superficial reflexes
Corneal reflex. Present. Present
Conjunctival reflex. Present. Present
Abdominal reflex. Present Present
Plantar reflex. Extensor. Flexor
Deep tendon reflexes
Biceps. +++. +
Triceps. +++. +
Supinator. +++ +
Knee. +++. +
Ankle. +++ +
BICEPS
TRICEPS
Sensory system:
Spinothalamic tract: touch, pain, and temperature sensations are normal
Posterior column: vibration, position, and fine touch normal.
Cortical sensations: Graphaesthesias and stereognosis absent.
No cerebellar signs.
Cardiovascular system:
S1, S2 heard
No murmurs
Respiratory system:
Bilateral air entry and Normal vesicular breath sounds were heard.
Per abdomen:
Soft and no organomegaly
Provisional diagnosis:
Cerebrovascular accident: Right-sided hemiparesis with Right UMN type of facial Palsy with Broca's aphasia secondary to left MCA territory involvement
Investigations:
Hemogram:
Hb: 15.7 gm/dl
TLC: 8,800 cells/cumm.
Platelets: 3.1 lakhs/cumm
RBS: 103mg/dl
LFT:
Total bilirubin: 0.64 mg/dl
Direct bilirubin : 0.18mg/dl
Total proteins:6.9
Albumin: 4.39
RFT:
Serum creatinine: 1.0 mg/dl
Blood urea:18mg/dl
Serum electrolytes: Normal
Fasting lipid profile: Normal
ESR: 20mm/hr
CRP: negative
APTT:34 sec
Bleeding time:2 min 30sec
Clotting time:4 min 30sec
D Dimer: 300 ug
RA factor: negative
CUE:
Albumin: Trace
Sugar: Nil
Pus cells:2-3cells/HPF
Epithelial cells:2-3cells/HPF
HIV: Non-Reactive
HbsAg: Non-reactive
VDRL: Negative
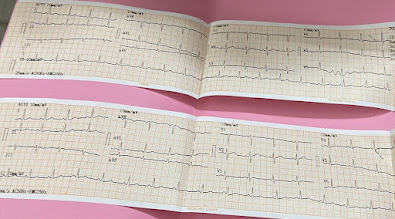
ECG:
12 lead ECG at 25 mm/sec showing sinus rhythm with regular RR interval with normal p wave QRS complex and T wave morphology
2d ECHO:
Normal LV systolic function
No regional wall motion abnormalities
EF: 62%
Chest x-ray :
Cxray PA views the inspiratory and non-rotated film.
Domes of the Diaphragm are clearly seen and well defined with no cardiomegaly
The right heart border and left heart border are clear with no Hilar lymphadenopathy or any Lymph node enlargement.
Bones and ribs appear normal.
MRI brain :
Final diagnosis:
Cerebrovascular accident: Right-sided hemiparesis with Right UMN type of facial Palsy with Broca's aphasia secondary to ischemic stroke involving left insula, temporal and front parietal regions (left MCA territory)
Treatment:
Physiotherapy of the right upper limb and lower limb.
Discussion:
Ischaemic stroke in young:
Definition:
Many authors consider the age of 45 years as the upper limit for stroke in young.
Epidemiology:
About 10-15% of strokes occur in younger patients, constituting approximately 2 million adolescents and young adults worldwide who suffer from an ischaemic stroke.
Risk factors:
Conventional risk factors like Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
Risk factors for stroke in young include smoking, alcohol, and drug abuse: cocaine IV drug users, and oral contraceptive pills.
Migraine with aura, Malignancy
Etiology:
1) Cardiac causes:
30% of stroke in young is secondary to cardiac causes: Congenital heart disease, PFO,
Atrial fibrillation, Acute MI, cardiomyopathy, Endocarditis, Cardiac tumors like atrial myxoma
2) Noninflammatory Nonatherosclerotic causes:
Arterial dissection, Marfans, Radition vasculopathy, Migraine, Fibromuscular dysplasia, CADASIL.
3) Inflammatory:
Takayasu arteritis, Giant cell arteritis, Kawasaki disease, PAN, Churg Strauss, Wegner, microscopic Polyangiitis.
4) Infections:
HIV, Tuberculosis, Hepatitis B, syphilis
5) Hypercoagulable states:
Protein C, protein S and antithrombin III deficiency, APLA, hyperhomocysteinemia, factor v leiden mutation, Sickle cell.
Approach to stroke in young:
|
CLINICAL CLUE |
SUSPICION |
|
Fever |
Infection |
|
Lymphadenopathy |
Lymphoma |
|
History of asthma |
Churg Strauss syndrome |
|
History of recent head trauma |
Arterial dissection |
|
Headache |
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical
infarcts and leukoencephalopathy |
|
Oral/genital ulcers |
Syphilis |
|
Butterfly erythema |
SLE |
|
Splinter hemorrhages underneath the nail |
Endocarditis |
|
Needle puncture signs |
Drug use |
|
Tattoos |
HIV infection |
|
Alopecia |
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) |
|
Xanthelasma |
Hyperlipidemia |
Investigations:
First-line investigations:
CBC, Lft, Rft, ECG, CXR, peripheral smear, ESR, CRP, HIV serology CT, MRI scan 2decho
Second-line investigations:
MR angiography, RA factor, serum homocysteine levels, protein C, protein S, Anca levels, factor V, Holter monitoring, D Dimer levels.
Treatment:
Treatment depends on the etiology of the stroke and once etiology is identified then treatment is individualized.
Antiplatelets are given.
Rehabilitation after stroke is a multidisciplinary approach with physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and speech-language therapists.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)







Comments
Post a Comment